Breast cancer
Definition
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor, i.e. a group of your own cells who lost ability to repair themself or to die, and will then grow uncontrollably, invading nearby parts of the body.
Breast cancer is one of the most common women cancers in France; around 42.000 cases are diagnosed every year. Major parts of women who develop breast cancer are between 50 and 70.
Although precise cause of breast cancer are unknown, we know what the main risk factors are: mainly age, early first menses or late menopause, lack of childbearing, high hormone level (more than 10 years of hormone therapy for post-menopause), and several toxins as alcohol, tobacco, diet and obesity.
Some genetic predispositions may play a role in developing breast cancer, with younger women and sometimes men.
Evolution :
Breast cancer usually begins with the formation of small tumor (abnormal cells aggregate), confined to the mammary ducts or lobules, without invasion of the surrounding tissue: at this stage, it is named lobular or ductal carcinoma in situ. Thanks to medicine progress, most breast cancers are diagnosed at this stage, allowing a high level rate of curing.
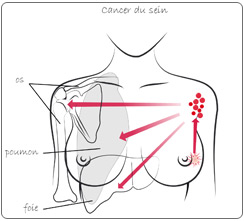
With no treatment, breast cancer will spread into the tissue, to become invasive carcinoma (locally infiltrated at an earlier stage). Then, malignant cells will spread through lymph channels to lymph nodes (axilla). It is the first stage of extra-mammal development of the main tumor. Once the lymph nodes will be invaded, this main tumor will be able to spread other malignant cells to other organs as liver, lung, bones: those distant tumors from the main one are called metastases.
Different type of exams – invasive or not – will allow to know the type of breast cancer, its aggressiveness, its weakness, its development stage and which nodes or organs are invaded, in order to give dedicated treatment
Breast cancer stages :
T0 : Non palpable tumor
T1 : Tumor less than 2 cm in size
T2 : Tumor between 2 and 5 cm
T3 : Tumor is larger than 5 cm
T4 : Tumor, regardless of the size, which has reached skin or pectoral muscle.
Diagnosis
Generally there are no symptoms of breast cancer and its diagnosis is based on mammography and regular breast exams, realized in France, every 2 years for women between 50 and 74. A thickening may be felt by a woman, and will be analyzed with a mammography. Some nipple discharges may be a base for diagnosis, especially with blood trace. Skin lesions usually appeared at a developed stage of breast cancer. A mammary pain is almost never due to breast cancer.
Breast cancer diagnosis will be realized by mammography and/or by breast ultrasound. Those non-invasive exams may be completed by a biopsy, in order to have a final result within few days.
Treatment
Surgery consists to remove the tumor, either by a lumpectomy or by a mastectomy. Axillary nodes will then be analyzed, looking for any trace of malignant cells.
For this surgery you will stay 1 week at the hospital and a 2 to 3 weeks of work leave will need to be planned.
After this first therapeutic stage, an extension work-up will be realized and multidisciplinary staff will decide complementary treatment such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy or hormone therapy.
Medical control
You will see your surgeon and oncologist every 4 months during 2 years, then every 6 months during 3 years, then every year with a mammography.
Breast cancer early diagnosed and treated is a good prognostic for complete curing.
Last update: 10/2/2013
