Chemotherapy
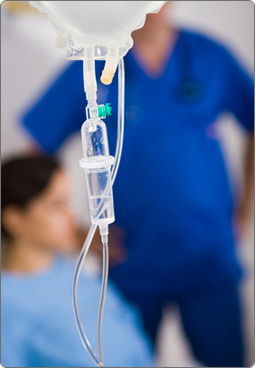
Chemotherapy is the use of medicine to destroy cancer cells.
Medicines used are put into blood so that they can travel to cells over the body. Procedure used to administrate chemotherapy is through a portacath: a small medical appliance that is installed beneath the skin ; a catheter connects the port to a vein (allowing to protect your veins). This treatment will directly target the tumor cells that could have spread everywhere in your body.
Chemotherapy is given during a half-day hospital stay, every week or every 2 weeks, or even every 3 weeks. Complete treatment time depends of the operating procedure designed by the chemotherapist. This will be explained to you during your first consultation: e.g. breast cancer chemotherapy operating procedure may include 6 cycles of chemotherapy, with a break every 3 weeks.
Chemotherapy can causes side effects (such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, mouth irritations, hair loss), as well as blood disorders detected by regular pre-therapy blood assessment.
Operating procedures for treatment are personalized, related to the disease and your health.
Last update: 10/2/2013
