Breast surgery
Adnexa surgery
Uterine surgery
Cervical surgery
Vulvar surgery
Other
Bartholin gland cyst surgery
Definition
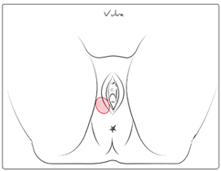
Bartholin glands are two pea sized glands located slightly posterior and to the left and the right of the vulva. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina. Usually those glands are not tangible. If the duct – allowing mucus secretion to be drained – becomes obstructed, a Bartholin’s cyst can develop, become infected and form an abscess.
Surgery Procedure
A general anesthesia will be given. Treating the abscess consists by draining the fluids out of it, that means making a small cut, cleaning with an antiseptic solution. The wound is kept open with a mesh left in place. A nurse at home will give personal care.
If a cystectomy is required – without any infection – duct and glands will be removed and the wound will be sutured with absorbable material.
Risks & Complications
In spite of the meticulous surgery technics, it is not possible to guarantee neither therapeutic success nor a total absence of any complications.
During the surgery
Blood loss: may rarely require a blood transfusion.
Post-surgery
- Bleeding of the wound (hemorrhage or hematoma) : rarely leads to another surgery.
- Altered sensations of the wound site. Some pain due to the healing process can also appear.
Last update: 10/2/2013
