Breast surgery
Adnexa surgery
Uterine surgery
Cervical surgery
Vulvar surgery
Other
Ectopic pregnancy
Definitions
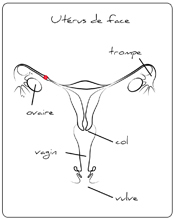
An ectopic pregnancy is a when the fertilized egg grows out of the uterine cavity, usually in the fallopian tube. It appears for 0,5% of the pregnancies, that is to say around 4.000 ectopic pregnancies per year in France. This can causes pelvic lateral pains and / or vaginal bleed. You may also feel no symptoms.
Risk factors of an ectopic pregnancy
Women with high level of risk are:
Women with any of the following event in their medical history:
- An ectopic pregnancy
- A pelvic inflammatory disease – PID (as salpingitis)
- A tubal surgery (plastic surgery, sterilization)
- Smoking
Women with a birth-control method as
- Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD)
- Progestogen-only pill
- Emergency contraceptive
Treatment
For most part of the ectopic pregnancies, the surgical treatment is performed by laparoscopy, under general anesthesia and in emergency. However in some critical or complex cases, a laparotomy (abdominal opening) may be required.
During the surgery, the practitioner will decide what to do on the fallopian tube damaged:
- Either remove the embryo (and the pregnancy tissue) for the fallopian tube,
- Or a salpingostomy : the ectopic growth is removed through a small, lengthwise cut in the fallopian tube.
- Or a salpingectomy: the fallopian tube is removed when damages are too important.
The hospital stay is usually from 2 to 3 days, and a work leave from 1 to 2 weeks is needed.
Last update: 10/2/2012
